They do not create strong biologically relevant interfaces with bones but they do promote strong adhesions to bones 3 the main applications of ceramic biomaterials include.
Degradation of ceramic biomaterials.
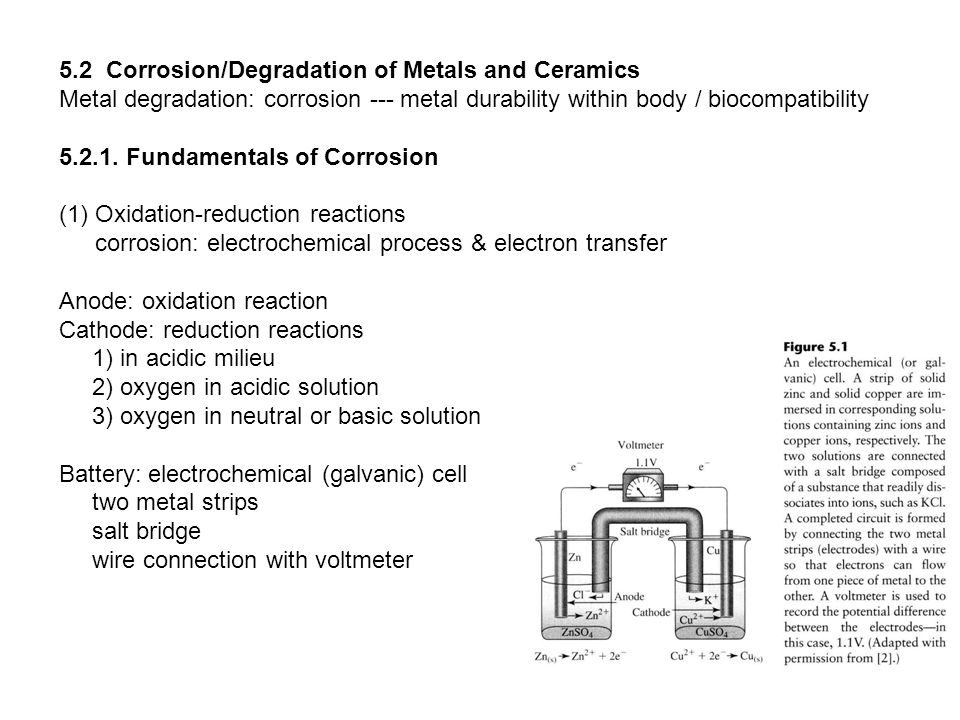
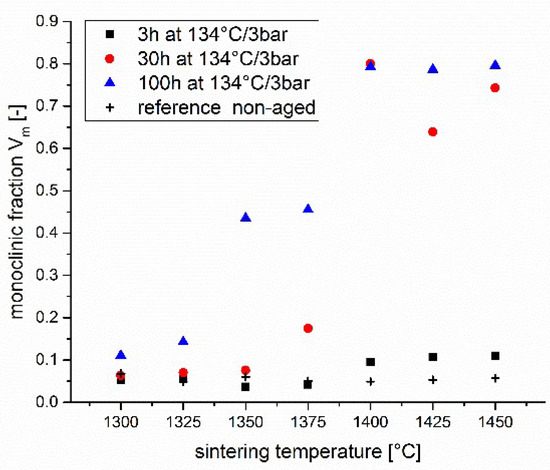
Even though the term corrosion was generally associated with metals ceramic materials are also undergone unintentional degradation in contact with environment.
Degradation of ceramic biomaterials unlike corrosion the passivation of a metal surface degradation which refers to the chemical breakdown of the bulk material occurs for ceramics however even this statement requires a caveat what we are referring to mostly for ceramics is dissolution not true degradation.
Among these composites ceramic polymer composites have been found to release toxic elements into the surrounding tissues.
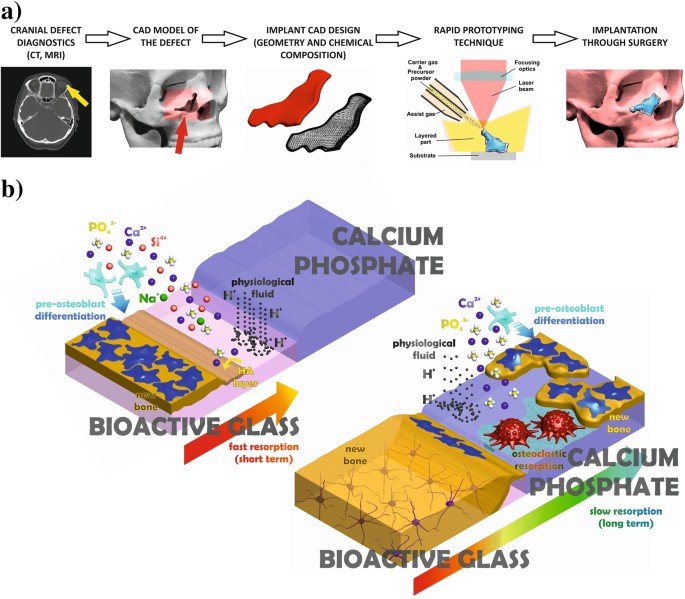
Ceramic biomaterials also stimulate bone growth and have low friction coefficients.
They can be crystalline or amorphous.
The crystalline and amorphous states are typical solid states which represent the degree of order between ions atoms or molecules.
Degradation mechanisms of bioceramics ceramic materials are held together by either ionic or covalent bonds.
Metals face corrosion related problems and ceramic coatings on metallic implants degrade over time during lengthy applications.
Ceramics provides current information on ceramics and their conversion from base materials to medical devices.
Ceramics provides current information on ceramics and their conversion from base materials to medical devices.
Initial chapters review biomedical applications and types of ceramics with subsequent sections focusing on the properties of ceramics and on corrosion degradation and wear of ceramic biomaterials.
Ceramic ceramic composites enjoy superiority due to similarity to bone minerals exhibiting biocompatibility and a readiness to be shaped.