Sedimentary organic carbon preservation there are several controls that affect the org c distribution in in sediments.
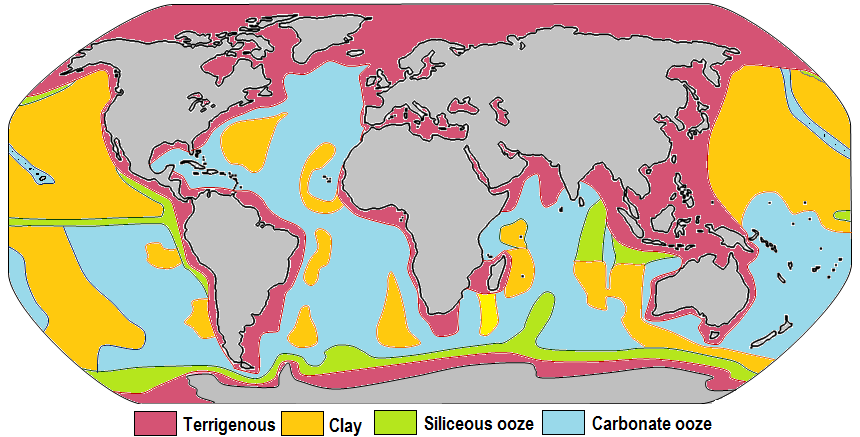
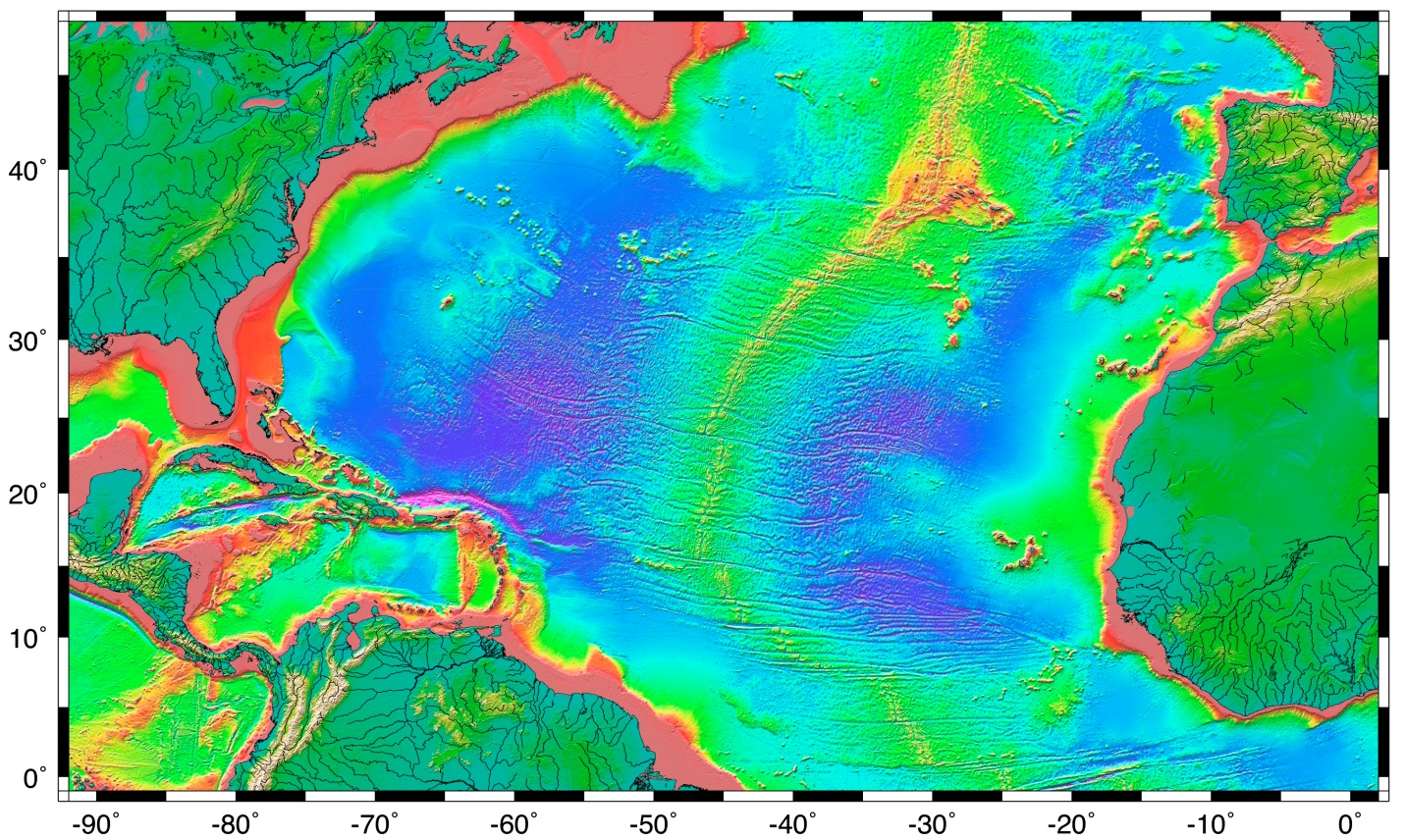
Distribution of sediment types on the ocean floor.
The size is from the smallest to largest these are.
Figure pageindex 1 shows the distribution of the major types of sediment on the ocean floor.
Clay less than or equal to 4 micrometer silt 4 to 62 micrometer sand 62 micrometer to 2 millimeter and more than 2 millimeter such.
Sandstone is an example of which of the following sediment types.
Pelagic sediment is composed of clay particles and microskeletons of marine organisms that settle slowly to the ocean floor.
In part 4 students develop a map showing the distribution of the primary marine sediment types of the pacific and.
Is not a random arrangement of these different sediment types.
The amount of organic matter preserved in the sediment depends on how much is produced and the preservation efficiency.
Sediment accumulation will depend on the the amount of material coming from the source the distance from the source the amount of time that sediment has had to.
Ocean basin ocean basin deep sea sediments.
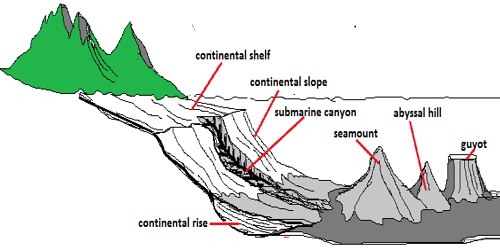
The ocean basin floor is everywhere covered by sediments of different types and origins.
Another classification of ocean floor sediments is by the size of the individual grain.
Lesson objectives earth science students will.
Biogenous sediment cosmogenous sediment hydrogenous sediment.
On average in the ocean only about 1 of the organic matter that sinks to the bottom of the ocean is preserved.
Define a deep sea sediment known as ooze and differentiate types of ooze based on composition 3.
They are useful for determining the distribution of ancient dinosaurs.
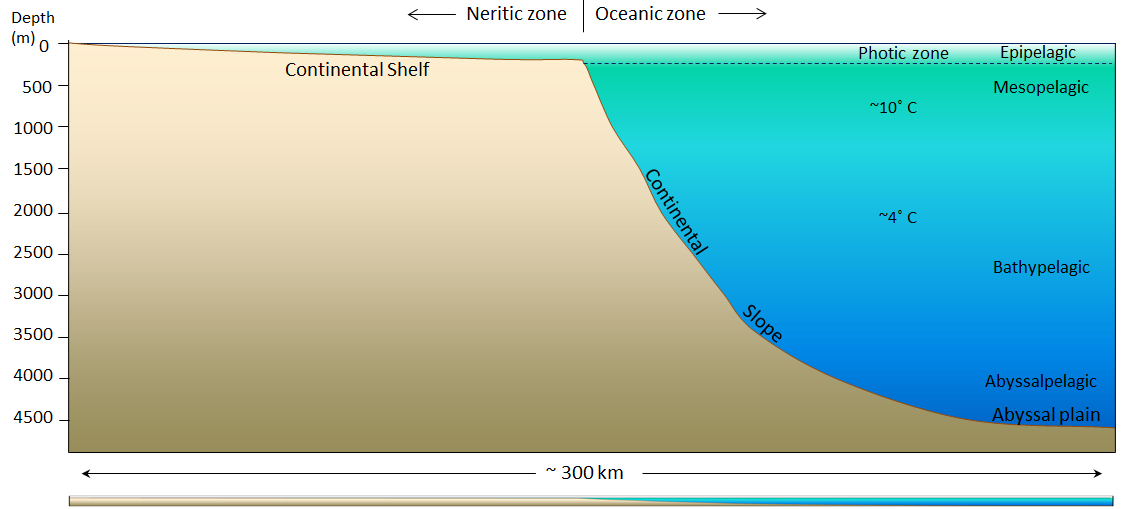
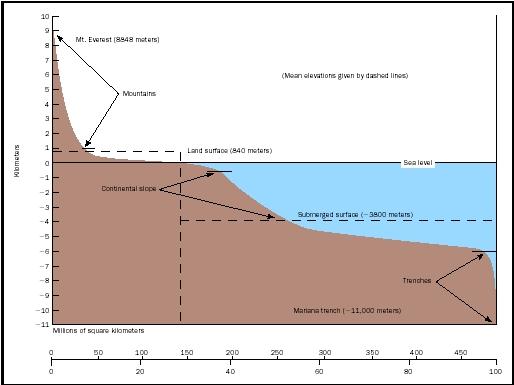
The area has low biological productivity and the ccd is at 4500 m depth.
It is further contoured by strong currents along the continental rise.
Distribution of sediment throughout the ocean.
Terrigenous sediment is derived from land and usually deposited on the continental shelf continental rise and abyssal plain.
You take a sediment sample from the ocean floor at a depth of 5500 m.
In parts 2 3 students observe and describe the physical characteristics of sediments cores and determine the composition using smear slide data and a decision tree.
Oceanographers have painstakingly mapped the distribution of sediment around the globe and have learned that at any given location the sediments provide important information regarding the history of the ocean as well as the overall state of climate on the.
The only exception are the crests of the spreading centres where new ocean floor has not existed long enough to accumulate a sediment cover.
Analyze and describe the distribution of sediment types throughout the ocean lesson contents 1.
12 6 sediment distribution now that we have an understanding of the types of sediments found in the ocean we can turn our attention to the processes that cause different types of sediments to dominate in different locations.
Identify the origins of different types of sediment 2.
Prior knowledge on sea floor sediments is explored in part 1.
Cosmogenous sediments could potentially end up in any part of the ocean but they accumulate in such small abundances that they are overwhelmed by other sediment types and thus are not dominant in any location.